What are Large-scale Generation Certificates (LGCs)?
What Are LGCs?
Large-scale Generation Certificates (LGCs) are a type of renewable energy certificate (REC) used in Australia to demonstrate that a certain amount of electricity has been generated from eligible renewable energy sources. They are created for every 1 MWh of eligible renewable energy generated and can be traded on the open market, allowing consumers and businesses to offset their greenhouse gas emissions by purchasing LGCs.
A basic example if you had a renewable energy system producing 100 MWh in a year it would generate
100 MWh x 1 = 100 LGCs
If at the time LGCs were worth $40 / LGC this would be $4,000 generated.
In general, the market price of LGCs fluctuates based on supply and demand. When there is a higher demand for LGCs, the price will typically be higher. Conversely, when supply and demand are high, the price will be lower.
In recent years, the price of LGCs has been relatively stable, fluctuating between $35 and $45. However, there have been some fluctuations, such as a significant drop in price in 2020, which was caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and its impact on the economy.
It is worth noting that the Australian government has set a target of 33,000 GWh of renewable energy generation by 2020 under the Renewable Energy Target (RET) and with the target already achieved, the government has not set any new targets yet which may have an impact on the demand and supply of LGCs in the future.
It's also worth noting that LGCs are a subset of the Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) and in recent years, the government has consulted on changes to the RET scheme and specifically LGCs, so the market may change in the future.
How do I forecast LGC revenue longer term?
With LGCs prices being subject to the supply & demands of buyers and moving around being able to accurately estimate what the forward estimate price will impact your cashflow calculations. The best way to forecast the expect pricing is to look at LGC futures and base the forward $/LGC price on these prices.
There are many providers that can provide forward estimates, however the best free to use data is from Mercari at the link below.
https://www.mercari.com.au/lgc-closing-rates/
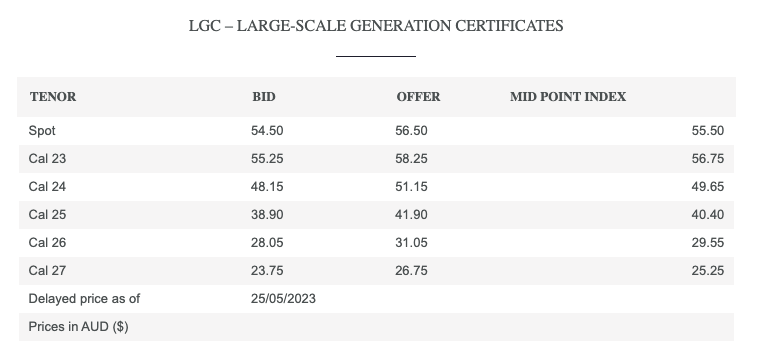
An example of the data provided is as below
Using the mid point index amount you are then able to use the estimated generation for the renewable energy system long term for the next 5 years and price in the expected LGC rates for your financial model. Note that if your going through a LGC traders you will need to associate about $1-$3/LGC for their processing fees based on site size.
Who Purchases LGCs?
In Australia, the largest purchasers of Large-scale Generation Certificates (LGCs) are typically large companies, such as energy retailers and heavy emitters, who use LGCs to offset their greenhouse gas emissions. These companies are required to buy LGCs as part of the Renewable Energy Target (RET) scheme, which sets a target for a certain percentage of Australia's electricity to come from renewable sources by a specific date.
Energy retailers are the largest buyers of LGCs in Australia, as they must purchase a certain number of LGCs each year to demonstrate that they are meeting their obligations under the RET scheme.
Other large buyers of LGCs include heavy emitters, such as cement and aluminium manufacturers, who also use LGCs to offset their emissions.
It's worth noting that the government is currently consulting on changes to the RET scheme and specifically LGCs, so the largest buyers of LGCs may change in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Large-scale Generation Certificates (LGCs) play a crucial role in Australia's renewable energy landscape. These certificates are issued for every megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity generated from eligible renewable energy sources. LGCs serve as proof that a certain amount of clean energy has been produced and can be traded on the market.
LGCs have multiple purposes. They incentivize the development of large-scale renewable energy projects, such as solar farms and wind farms, by providing a financial value for the clean energy they generate. LGCs also enable consumers and businesses to offset their greenhouse gas emissions by purchasing these certificates, thus promoting environmental sustainability.
Energy retailers are major purchasers of LGCs, as they are obliged to meet renewable energy targets set by the government. Additionally, heavy emitters, including industries like cement and aluminum manufacturing, utilize LGCs to offset their emissions and contribute to their sustainability commitments.
While the future of the LGC scheme remains uncertain, its current implementation has been instrumental in driving renewable energy growth in Australia. The scheme has played a vital role in encouraging the transition to a cleaner energy mix and reducing the country's carbon footprint.
As Australia continues its journey towards a more sustainable future, LGCs will likely remain a critical instrument in promoting renewable energy generation and fostering a greener economy.